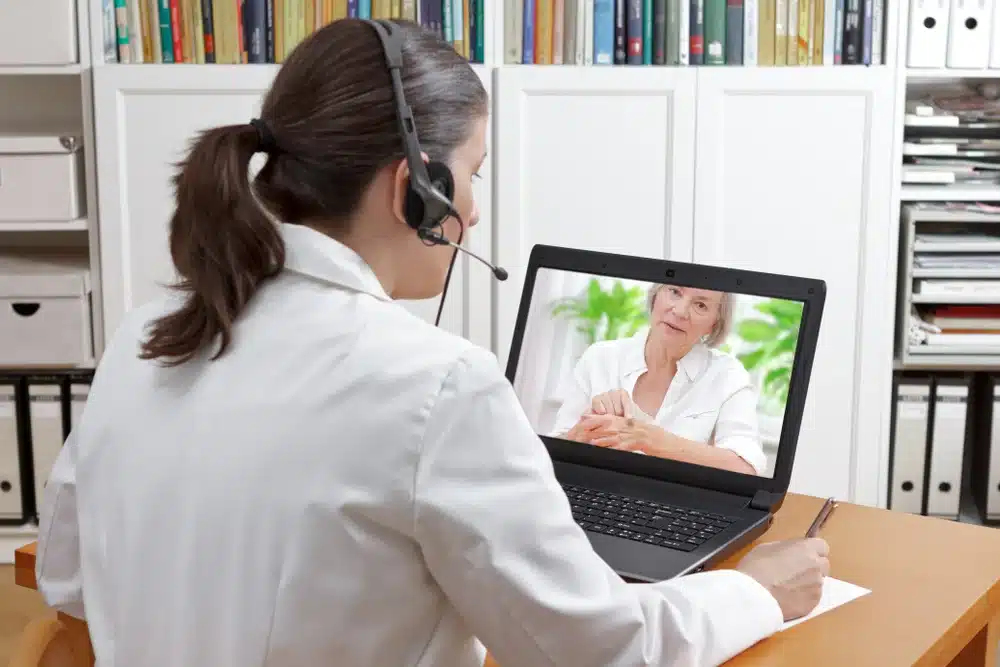
Liposuction is a popular cosmetic procedure that helps reshape the body in a way that many people seek, similar to how cochlear implants assist hearing patients. For patients with hearing or vision impairments, communication strategies are vital to ensure a smooth experience. Historically, these patients faced challenges in understanding medical information and procedures. Today, healthcare providers recognize the importance of clear communication tailored to their needs.
Effective strategies include using visual aids, written instructions, and interpreters when necessary. These methods enhance understanding and build trust between patients and medical teams. By focusing on communication, including active listening strategies, we can help all patients feel confident and informed about their liposuction journey. This post will explore practical tips for improving communication with patients who have sensory impairments during the liposuction process.
Key Takeaways
- Use clear and simple language, along with good communication strategies and proper communication strategies, when communicating with patients who have hearing or vision impairments to ensure communication success and understanding through active listening strategies.
- Prepare for appointments by asking patients about their preferred communication methods, including active listening strategies and accommodating disabilities with hearing devices or hearing aids, allowing for a more personalized experience.
- Enhance reception and waiting areas by using good communication strategies, proper communication strategies, visual aids, and clear signage to help patients navigate the space easily with active listening strategies for communication success.
- During appointments, employ good communication strategies and active listening strategies such as tapping gently on the shoulder to gain the patient’s attention before speaking for communication success.
- Maintain eye contact and articulate your speech clearly, which helps patients with hearing impairments better understand what you are saying, as these are good communication strategies for communication success.
- Train staff on effective communication strategies to create a welcoming environment for patients with hearing or vision impairments, ensuring they feel valued and understood.
Understanding Hearing and Vision Impairments
Types of Impairments
Hearing impairments vary widely. They can range from mild to profound hearing loss. Mild hearing loss may only affect some sounds, while profound hearing loss means a person cannot hear anything at all, making active listening strategies and good communication strategies essential. Many deaf individuals use hearing aids to assist in communication. These devices amplify sounds and help the user engage with their environment.
Vision impairments also come in different forms. Some people may have low vision, which makes it hard to see details. Others may be completely blind. Each type of impairment, such as those requiring a hearing aid, affects daily life in unique ways, highlighting the importance of good communication strategies. For instance, deaf patients might struggle to follow conversations without visual cues. Blind individuals may face difficulties navigating spaces or recognizing faces.
Impact on Daily Life
Living with hearing or vision impairments can be challenging. Communication often becomes complicated. Deaf individuals may rely on sign language, lip-reading, hearing aids, or good communication strategies to understand others. This reliance can create barriers if the people around them are not familiar with these methods.
Daily tasks can also become more difficult. A deaf child might miss important instructions in a classroom setting. Similarly, someone with low vision may struggle to read labels or signs. These challenges highlight the importance of accommodating individuals with impairments in various settings, especially healthcare.
Importance in Healthcare
Recognizing these impairments in healthcare is crucial. Medical professionals must understand how hearing and vision challenges impact patient care. Effective communication strategies are essential for accurate assessments and treatment plans.
For example, during a hearing evaluation, doctors should ensure that deaf patients understand the process. Using visual aids or written instructions can help bridge communication gaps. Providing interpreters can enhance understanding during consultations.
Common Misconceptions
Many misconceptions surround hearing and vision impairments. One common belief is that all deaf individuals cannot hear anything at all. In reality, some people may have residual hearing and benefit from hearing devices.
Another misconception is that vision impairments only affect older adults. However, children can also experience vision loss due to various conditions like amblyopia or retinopathy of prematurity.
These misunderstandings can lead to inadequate support for patients with disabilities. It’s vital for healthcare providers to educate themselves about these issues to offer better care.
Preparing for the Appointment
Inform the Clinic
Patients should inform the clinic about their impairment needs before the appointment. This notice helps staff prepare for effective communication. Clinics can adjust their approach based on these needs. For example, they may provide interpreters or visual materials.
Sharing this information allows clinics to create a more comfortable environment. It ensures that patients receive the best possible care. Patients can also mention if they need specific accommodations during the procedure.
Bring Necessary Aids
Bringing necessary aids is crucial for effective communication. Patients with hearing impairments should carry their hearing devices. These devices help them understand conversations better. Visual aids can assist patients with vision impairments in reading important information.
Patients might also consider bringing a family member or friend for support. This person can help communicate questions and concerns during the appointment. Having someone familiar can ease anxiety and enhance understanding.
Prepare Questions
Preparing questions ahead of time is essential. Patients should list their concerns about the procedure. They may want to ask about risks or recovery times. Writing down these questions helps ensure clarity during discussions.
Patients should also inquire about post-operative care. Understanding what to expect after surgery is vital for recovery. Preparing in advance allows patients to feel more confident in their decisions.
Consideration of Communication Styles
Communication styles vary among individuals, especially for those with impairments. Some patients may prefer written communication while others may benefit from verbal explanations. Discussing preferred communication methods with the clinic staff can improve interactions.
Clinics often have resources available to aid communication. For instance, they might use large print materials or audio descriptions. Knowing what works best for each patient enhances understanding and comfort.
Follow-Up Appointments
Follow-up appointments are important for monitoring progress post-surgery. Patients should continue to communicate their needs during these visits as well. Regular check-ins allow healthcare providers to address any concerns effectively.
Patients should not hesitate to express difficulties they face after surgery. Open dialogue promotes better outcomes and satisfaction with care received.
Enhancing Reception and Waiting Areas
Visual Aids
Installing visual aids or screens can significantly enhance communication for patients with hearing impairments. These screens can display important announcements, appointment times, and instructions. Clear visuals help ensure that patients receive crucial information without relying solely on audio announcements.
For example, a hospital could set up large digital displays in the waiting area. These displays can scroll through updates in real-time. Patients will appreciate knowing when it’s their turn without needing to strain to hear an announcement.
Quieter Spaces
Creating quieter spaces within reception areas is essential. Background noise can be distracting for patients who rely on lip-reading or visual cues. Reducing noise levels allows patients to focus better on their surroundings and conversations.
Consider using sound-absorbing materials in walls and ceilings. This change can help lower overall noise levels. Designated quiet zones can provide a peaceful environment for those waiting for their appointments.
Clear Signage
Clear signage is vital for navigation in medical facilities. Patients with vision impairments often need tactile markers and well-lit signs to move around confidently. Signs should use large fonts and high-contrast colors for better visibility.
Tactile markers can guide visually impaired patients to key areas like restrooms, examination rooms, and exits. For instance, raised letters or braille on signs can offer critical information at a touch. Staff should also be trained to assist these patients effectively.
Communication Tools
Communication tools can further improve the experience of patients with hearing or vision impairments. Facilities should consider providing tablets or devices equipped with speech-to-text applications. These tools allow staff and patients to communicate more easily during consultations.
Offering written materials in accessible formats is another step forward. Braille brochures or large print handouts can provide essential information about procedures and policies.
Staff Training
Training staff members on how to interact with patients who have sensory impairments is crucial. Staff should learn effective communication strategies tailored to individual needs. Simple techniques like facing the patient directly while speaking can make a significant difference.
Regular workshops can keep staff informed about best practices for assisting these patients. Understanding the challenges faced by individuals with hearing or vision impairments fosters a supportive environment.
Effective Communication During Appointments
Face-to-Face Interaction
Face-to-face interaction is crucial for effective communication. Patients with hearing or vision impairments benefit from seeing the provider’s facial expressions. Maintaining eye contact helps establish a connection. It shows attentiveness and respect.
Providers should position themselves at eye level with the patient. This approach makes communication easier and more comfortable. Avoiding barriers between the provider and the patient can enhance understanding. For example, sitting across a table can obstruct visual cues.
Simple Language
Using simple language is an important strategy. Medical jargon can confuse patients, especially those with impairments. Clear articulation of words aids in comprehension. Providers should avoid long sentences and complex phrases.
Communication success relies on being straightforward. For instance, instead of saying “We will conduct a comprehensive evaluation,” say “We will check your health.” This clarity reduces anxiety and builds trust.
Verifying Understanding
Verifying understanding is essential for effective communication. Providers should encourage feedback from patients. Asking patients to repeat instructions ensures they grasp the information. This method also allows providers to clarify any misunderstandings.
Providers might ask questions like, “Can you tell me what we discussed?” This strategy confirms that the patient understands their treatment plan. It also encourages active participation in their care.
Non-Verbal Cues
Non-verbal cues play a significant role in communication strategies. Gestures, facial expressions, and body language can convey messages without words. Providers should be aware of their own non-verbal signals as well.
For example, nodding can indicate agreement or encouragement. Similarly, smiling can create a welcoming atmosphere. These actions help make patients feel more comfortable during appointments.
Assistive Tools
Assistive tools can enhance communication for patients with impairments. Hearing aids, magnifiers, or note-taking apps may be beneficial. Providers should inquire if patients need these tools ahead of time.
Offering written materials can also aid understanding. Providing brochures in large print or easy-to-read formats helps ensure access to necessary information.
Training Staff
Training staff on effective communication strategies is vital. All team members should be aware of how to interact with patients who have hearing or vision impairments. Regular workshops on proper communication skills can improve overall patient experience.
Encouraging staff to practice active listening techniques enhances interactions too. This practice allows them to respond appropriately to patient needs.
Techniques for Gaining Patient Attention
Physical Cues
Gentle physical cues help in gaining the attention of patients with hearing or vision impairments. A light touch on the shoulder can signal that you wish to communicate. This method is non-intrusive and respectful.
Visual signals also play a crucial role. Waving your hand or using gestures can effectively catch the patient’s eye. Ensure that these cues are clear and easily understandable.
Before starting any conversation, let the patient know that you are about to speak. This prepares them for interaction. It can make them feel more comfortable and engaged.
Verbal Communication
Verbal communication needs special attention in these situations. Speak clearly and at a moderate pace. Avoid mumbling or speaking too quickly, as this may confuse the patient.
Using the patient’s name can help focus their attention. It creates a personal connection and shows that you value their presence.
Asking open-ended questions encourages participation. This allows patients to express their needs or concerns more freely. Listening actively is essential during this process.
Sensory Considerations
Avoid sudden movements or loud noises around patients with sensory impairments. These actions can startle them and disrupt communication. Instead, maintain a calm environment to facilitate better interactions.
When communicating, ensure that lighting is adequate if the patient has vision issues. Good lighting helps them see facial expressions and gestures better.
For patients with hearing impairments, reduce background noise when possible. This makes it easier for them to focus on your voice.
Active Listening Strategies
Active listening strategies enhance understanding during conversations. Show that you are engaged by nodding or making affirming sounds. This encourages patients to share more information.
Rephrasing what the patient says can confirm your understanding. It also reassures them that their thoughts are valued and heard.
Encouraging feedback is vital as well. Ask if they need clarification on anything discussed. This fosters an open line of communication and builds trust.
Building Rapport
Building rapport takes time but is crucial for effective communication. Start with small talk to create a relaxed atmosphere before discussing medical topics.
Establishing trust allows patients to feel safe in expressing their concerns. They will be more likely to share important information about their health.
Involve family members or caregivers when appropriate. They can provide additional support and help bridge any communication gaps.
Importance of Clear Speech and Eye Contact
Clear Speech
Speaking slowly and clearly is essential. Patients with hearing or vision impairments may struggle to understand fast speech. Clear articulation helps them grasp the information better. Use simple words and short sentences. This approach reduces confusion.
Consider the patient’s comfort level. Some may require extra time to process what you say. Patience is key here. Repeating important points can also help reinforce understanding. Avoid using jargon or complex medical terms. Instead, use straightforward language that everyone can comprehend.
Eye Contact
Eye contact plays a crucial role in effective communication. It builds trust between the speaker and the patient. Maintaining eye contact shows attentiveness and respect for their needs. It signals that you value their presence and input.
For patients with hearing impairments, eye contact becomes even more vital. They often rely on lip-reading to understand spoken words. Looking directly at them ensures they can see your mouth movements clearly. This practice enhances their ability to follow the conversation.
Avoiding Barriers
Avoid covering your mouth while speaking. This action obstructs clear communication. It prevents patients from reading lips and diminishes sound clarity for those who rely on hearing aids.
Turning away while talking can also create barriers. It disrupts the flow of communication and can lead to misunderstandings. Always face the patient when speaking to them.
Use gestures to support your message as well. Simple hand movements can enhance understanding. For instance, pointing to relevant items can clarify instructions or explanations.

Additional Tips
- Check for comprehension regularly: Ask questions to ensure the patient understands.
- Be aware of your environment: Reduce background noise when possible to prevent distractions.
- Provide written materials: Handouts that summarize key points can be helpful.
- Encourage questions: Invite patients to ask about anything they don’t understand.
Alternative Communication Methods
Sign Language Interpreters
Sign language interpreters play a crucial role for patients with hearing impairments. They bridge the gap between medical staff and patients. Using sign language ensures that patients fully understand the information shared during consultations or procedures. This method allows for effective communication without relying solely on spoken words.
Written communication also serves as an important tool. It can include notes, pamphlets, or printed instructions. These materials provide clear information and allow patients to review details at their own pace. This approach minimizes misunderstandings that can arise from verbal exchanges.
Technology-Assisted Methods
Technology offers various solutions to enhance communication access. Speech-to-text apps convert spoken words into written text in real-time. Patients can read what is being said during discussions with healthcare providers. This method empowers them to engage actively in their care.
Assistive listening devices are another valuable option for patients with hearing loss. These devices amplify sound, making it easier for patients to hear conversations. They can be used during appointments to improve understanding and reduce communication barriers.
Visual Aids and Demonstration Tools
Visual aids significantly enhance comprehension for patients with vision impairments. Using diagrams, pictures, or videos can clarify complex information. Healthcare providers should incorporate these tools into their presentations whenever possible.
Demonstration tools also prove effective in conveying important concepts. For example, showing how a procedure works through visual means can alleviate patient anxiety. Patients often feel more comfortable when they understand what will happen during their treatment.
Preferred Communication Methods
Identifying preferred communication methods is essential for effective interactions. Healthcare providers should ask patients about their preferred ways of receiving information. Some may prefer written materials, while others might benefit from visual aids or technology-assisted options.
Creating an environment that supports communication access is vital. Providers must be adaptable and willing to use various methods based on individual needs. This flexibility fosters trust and encourages open dialogue between patients and healthcare professionals.
Overcoming Communication Barriers
Addressing communication barriers requires effort from both sides. Healthcare providers must be patient and attentive to the needs of their patients. Encouraging questions helps clarify any confusion that may arise during discussions.
Using a combination of methods often yields the best results. For instance, pairing sign language interpreting with written materials can reinforce understanding. This multi-faceted approach supports diverse learning styles and enhances overall patient care.
Training Staff for Better Interaction
Skills Development
Regular training sessions on disability awareness are essential. Staff should learn about the unique needs of patients with hearing or vision impairments. This training can improve communication and build trust. Empathy and patience are key skills that staff must develop. Understanding the challenges these patients face helps staff respond better. For example, a patient with hearing loss may need visual cues or written instructions. Training should include role-playing scenarios to practice these skills.
Partnerships with Organizations
Collaboration with disabled people’s organizations is beneficial. These partnerships provide valuable insights into effective communication strategies. Organizations often have resources and experts who can guide staff training. They can share experiences from patients, helping staff understand their perspectives. This collaboration can also lead to improved services tailored to specific needs. Engaging with these groups fosters a supportive environment for both patients and staff.
Use of Interpreters
Utilizing interpreters can enhance communication significantly. Staff should know when to involve an interpreter for effective interaction. An interpreter can bridge the gap between medical staff and patients with hearing impairments. This ensures that patients fully understand their treatment options and procedures. Staff must be trained to work alongside interpreters effectively. They should learn how to direct questions to the patient, not the interpreter, to maintain clear communication.
Addressing Loss of Vision
For patients with vision impairments, staff should focus on verbal communication. Describing surroundings and procedures helps these patients navigate their environment safely. Staff should avoid using vague terms like “over there.” Instead, they can provide specific directions or descriptions. Regular training on how to assist visually impaired patients is necessary. This includes understanding how to offer physical support when needed.
Creating an Inclusive Environment
Building an inclusive environment requires ongoing effort from all staff members. Everyone should feel responsible for fostering communication with patients who have disabilities. Regular meetings can help staff share experiences and discuss challenges they face. This team approach promotes a culture of understanding and support within the facility.
Summary
You’ve learned how to support patients with hearing or vision impairments during their liposuction journey. By understanding their unique needs, preparing effectively, and using clear communication strategies, you can significantly enhance their experience. Your attention to detail in reception areas and staff training plays a vital role in ensuring comfort and trust.
Now, it’s time to put these strategies into action. Make your practice a welcoming space for all patients. Emphasize clear speech, eye contact, and alternative communication methods. These small changes can lead to big improvements in patient satisfaction and outcomes. Commit to ongoing training for your team. Together, you can create an inclusive environment that empowers every patient. Let’s make a difference!
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I know about hearing and vision impairments before a liposuction appointment?
Understanding the specific needs of patients with hearing and vision impairments is crucial. Each patient may require tailored communication strategies to ensure comfort and clarity throughout the process.
How can I prepare for my liposuction appointment if I have an impairment?
Inform your healthcare provider in advance about your impairment. This allows them to implement appropriate communication methods and accommodations, ensuring a smoother experience.
What improvements can be made in reception and waiting areas for impaired patients?
Reception and waiting areas should have clear signage, adequate lighting, and seating arrangements that facilitate interaction. Staff should be trained to assist patients effectively.
What are effective communication techniques during appointments?
Use simple language, speak clearly, and maintain eye contact. Always check for understanding and encourage questions to foster an open dialogue.
How can staff gain the attention of patients with impairments?
Staff should use visual cues, such as waving or gesturing, and approach patients from a visible angle. This helps ensure they are noticed before initiating conversation.
Why is clear speech and eye contact important in communication?
Clear speech reduces misunderstandings, while eye contact builds trust and shows attentiveness. Both enhance engagement between healthcare providers and patients.
What alternative communication methods can be used?
Consider using written notes, sign language interpreters, or visual aids. These methods can bridge communication gaps effectively, ensuring all patients feel included.