Fat transfer for breast reconstruction offers a natural alternative to implants. Many women seek this option after surgery or trauma. Unlike traditional methods, fat transfer, often used in autologous breast reconstruction, uses your own body fat through grafting, creating a more organic look and feel in breast reconstruction surgery and breast reconstructions. This technique not only enhances breast volume but also improves body contours.
Patients often prefer it due to fewer complications and a shorter recovery time. The results of the breast augmentation method can be long-lasting, boosting confidence and self-image during the breast augmentation journey. While implants may involve risks like rupture, fat transfer minimizes these concerns. Understanding the advantages of fat transfer can empower women in their reconstruction journey.
Key Takeaways
- Consider Fat Transfer: If you’re looking for a natural option for breast reconstruction, fat transfer can be a suitable choice. Discuss this with your doctor to see if it fits your needs in your breast augmentation journey, including options like breast implants or a fat injection procedure, such as fat transfer breast augmentation.
- Know the Benefits: Fat transfer not only enhances breast shape through grafting but also uses your own body fat, reducing the risk of rejection. This can lead to a more natural feel and appearance.
- Understand Permanence: While fat transfer, like breast implants, can provide long-lasting results in your breast augmentation journey, some fat may be reabsorbed by your body over time. Be prepared for potential touch-up procedures.
- Be Aware of Risks: Like any surgery, fat transfer has risks such as infection or necrosis, similar to those associated with breast implants. Make sure to discuss these with your surgeon to weigh the benefits and risks.
- Assess Suitability: Not everyone is a good candidate for fat transfer. Factors like overall health and body fat availability play a role, so consult with a specialist to evaluate your situation.
- Prepare for Recovery: Recovery from structural fat grafting varies by individual, but following pre-procedure steps and post-operative care is crucial for optimal healing and results.
Understanding Fat Transfer
What is Fat Transfer?
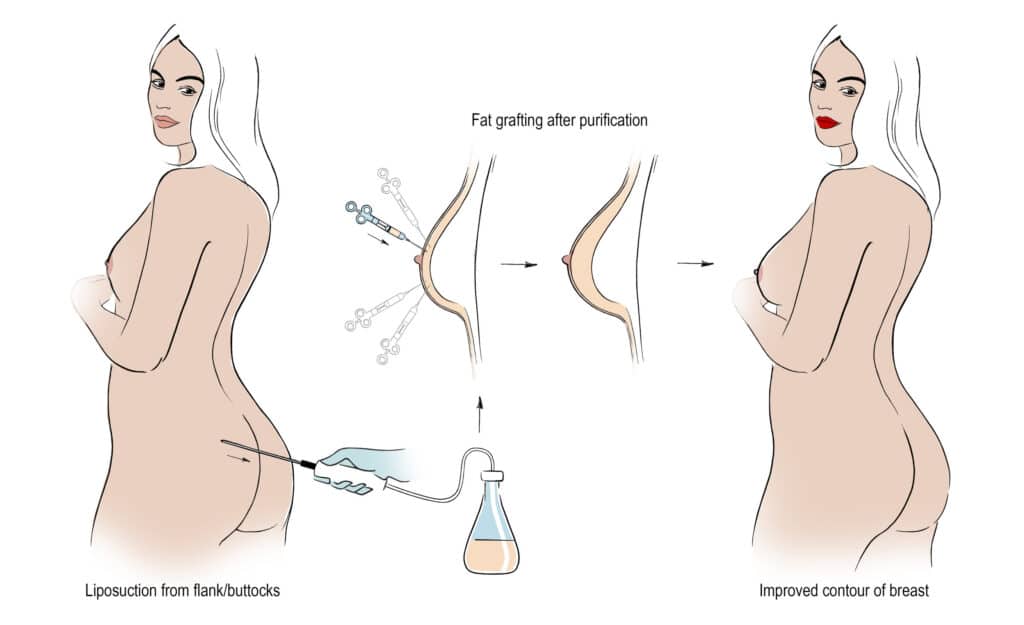
Fat transfer is a method used in breast reconstruction. This technique involves taking fat from one area of the body and injecting it into the breast. The process aims to restore volume and shape after surgery or trauma using structural fat grafting.
Harvesting Process
Surgeons first harvest fat from areas like the abdomen, thighs, or flanks. They use liposuction to remove the fat. This process is minimally invasive and leaves small scars. The harvested fat is then purified to prepare it for injection.
After purification, the fat is injected into the breast area. Surgeons carefully place the transferred fat to create a natural contour. They often use a series of small injections, including structural fat grafting, to achieve even distribution.
Achieving Natural Appearance
The main goal of fat transfer is to achieve a natural look and feel in reconstructed breasts. Unlike implants, which can sometimes feel artificial, transferred fat integrates with existing tissue. This integration helps in creating a more realistic appearance.
Patients often report satisfaction with the results. They appreciate not only the aesthetic improvements from structural fat grafting but also the softer texture of their reconstructed breasts.
Fat transfer can also be combined with other techniques. For example, some patients may choose implants along with fat transfers for added volume. This combination can enhance overall results.
Benefits of Fat Transfer
Fat transfer offers several benefits for breast reconstruction:
- Natural Results: The procedure provides a more organic look through structural fat grafting compared to traditional implants.
- Dual Benefit: Patients can slim down other body parts while enhancing breast volume through structural fat grafting.
- Less Recovery Time: Compared to structural fat grafting and implant surgery, recovery time tends to be shorter.
- Minimal Scarring: Liposuction leaves smaller scars than larger incisions used for implants, unlike structural fat grafting.
Considerations
Not every patient is a candidate for fat transfer. Factors such as structural fat grafting, body type, and overall health play a role in determining eligibility. Surgeons evaluate these aspects during consultations.
e patients may require multiple sessions of structural fat grafting to achieve desired results. Each session allows for additional fat to be transferred as needed.
Overall, fat transfer is an effective option for breast reconstruction. It provides women with a way to regain their confidence after surgery or trauma, including structural fat grafting.
Benefits of Fat Transfer
Autologous Tissue
Fat transfer uses the patient’s own tissue. This method significantly reduces the risk of rejection. The body recognizes its own fat, making it less likely to cause complications. This is a key advantage over synthetic implants. Patients benefit from a more seamless integration of the grafted fat.
Is Fat Transfer Permanent
Longevity of Results
Fat transfer for breast reconstruction offers long-lasting results. However, some fat may be reabsorbed by the body over time. Studies indicate that around 30% to 50% of transferred fat may not survive after the procedure. This can lead to a change in volume and shape.
Patients often experience a gradual adjustment as their bodies adapt to the new fat. The process of reabsorption varies from person to person. Factors like individual metabolism and blood supply to the area play significant roles in how much fat remains.
Multiple Sessions
Maintaining the desired results from fat transfer might require multiple sessions. Surgeons often recommend follow-up procedures for optimal outcomes. Each session allows for additional fat to be placed where it is needed most.
Patients should discuss their goals with their surgeon. This conversation helps set realistic expectations about the number of procedures required. Surgeons may suggest timing between sessions based on individual recovery rates.
Influencing Factors
Several factors can influence how permanent the results of fat transfer are. Weight fluctuations are one of the primary concerns. Gaining or losing weight can affect breast size and shape after the procedure.
Lifestyle choices also impact longevity. Regular exercise and a balanced diet help maintain stable weight. Smoking can hinder blood flow and affect healing, which may lead to more fat being reabsorbed.
Hormonal changes can also play a role in how long results last. Changes during pregnancy or menopause might alter body composition and fat storage patterns.
Risks and Considerations
Potential Complications
Fat transfer for breast reconstruction carries some risks. One major concern is infection at the injection sites. Infection can lead to further complications and may require additional treatment. Cyst formation is another potential issue. Cysts can develop in the transferred fat, causing discomfort or requiring surgical intervention.
Patients should also be aware of the possibility of fat cell migration. This occurs when the transferred fat moves from its original location. It can affect the final appearance of the breast. Microcalcification may occur within the fat tissue. This condition can complicate future mammograms and raise concerns about breast cancer detection.
Importance of Consultation
Consulting with a qualified surgeon is crucial. A skilled professional can help minimize risks associated with fat transfer procedures. They will assess individual health conditions and discuss specific risks related to each case.
Surgeons often use advanced techniques to enhance safety and improve results. They may suggest combining fat transfer with implants for better outcomes. This approach can provide more volume and improve symmetry in breast reconstruction.
Evaluating Benefits and Costs
The benefits of fat transfer include a natural look and feel compared to implants. Many patients prefer this technique due to its less invasive nature. However, costs can vary significantly based on several factors. These include the surgeon’s experience, geographic location, and whether additional procedures are needed.
Insurance coverage for fat transfer varies widely. Some plans may cover it if deemed medically necessary after breast cancer surgery. Others may not cover it at all, as it is often considered cosmetic.
Long-Term Results
Long-term results from fat transfer can differ among patients. Factors influencing results include age, skin quality, and overall health. Some patients may require touch-up procedures over time as the body absorbs some of the transferred fat.
Monitoring results is essential after surgery. Regular follow-ups with your surgeon will help identify any complications early.
Understanding Necrosis
Definition
Necrosis refers to the death of cells or tissues. This process can occur due to various factors, including lack of blood flow. In fat grafting procedures, necrosis can happen when the transferred fat cells do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients.
Causes in Fat Grafting
Fat grafting necrosis is a potential risk during breast reconstruction. The body may not accept the transplanted fat if it lacks adequate blood supply. Factors like smoking, diabetes, or poor circulation increase this risk. Affected areas may become firm or hard, indicating that tissue is dying.
Impact on Tissue
Necrosis can lead to complications such as scar tissue formation. Scar tissue develops as the body attempts to heal the damaged area. This scar tissue can create lumps that resemble cancerous growths. Patients might feel anxious when they discover these lumps. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments help manage concerns.
Treatment Options
Several treatment options exist for managing necrosis after fat transfer. Excision is one method where a surgeon removes dead tissue. This procedure helps prevent further complications and improves appearance.
Aspiration is another option for addressing necrotic areas. Doctors use a needle to remove fluid from lumps caused by necrosis. This method can alleviate discomfort and reduce the size of the lump.
Importance of Monitoring
Monitoring for signs of necrosis is crucial after fat grafting surgery. Patients should watch for changes in the treated area, such as unusual swelling or discoloration. Early detection leads to better outcomes and less invasive treatments.
Emotional Considerations
Experiencing complications like necrosis can be emotionally challenging for patients. Concerns about health and body image often arise after surgery. Support groups or counseling may provide comfort and reassurance during recovery.
Suitability for You
Consultation
A consultation with a qualified surgeon is crucial. Surgeons assess individual suitability for fat transfer during this meeting. They evaluate medical history and previous surgeries. This process helps determine if the procedure is appropriate.
Surgeons will also discuss your health status. They look at any existing conditions that may affect recovery. Understanding your overall health is important for safety.
Body Fat Availability
Body fat availability plays a significant role in the decision. Not everyone has enough fat to use as a donor site. A good candidate should have sufficient fat in areas like the abdomen or thighs.
Surgeons often use liposuction to harvest fat from these sites. They then inject the fat into the breast area. If there isn’t enough body fat, other options may be explored.
Personal Goals
Discussing personal goals is essential for successful outcomes. People should clearly state their expectations for the procedure. Some may want a modest enhancement, while others seek more significant changes.
Understanding your goals helps align them with realistic results. This ensures that both you and your surgeon are on the same page. Clear communication can lead to better satisfaction after the procedure.
Overall Health Status
Overall health status affects suitability for fat transfer. Surgeons consider factors such as age and lifestyle choices. Smokers may face higher risks during recovery. Weight fluctuations can also impact results.
Maintaining a stable weight before surgery is recommended. This stability helps ensure better outcomes and longevity of results.
Recovery Considerations
Recovery involves some downtime and care. Patients must follow post-operative instructions closely. Stitches may be necessary at the donor site, which requires attention.
Surgeons provide specific guidelines for managing pain and swelling. Adhering to these recommendations promotes healing and reduces complications.
Emotional Factors
Emotional readiness is another important aspect. Undergoing breast reconstruction can be an emotional journey. It’s vital to prepare mentally for changes in appearance.
Support from friends and family can help ease anxiety about the process. Engaging in support groups may also offer comfort and guidance.
Pre-Procedure Steps
Medical Evaluation
Surgeons recommend a thorough medical evaluation before any invasive procedure. This assessment helps identify any underlying health issues. It also ensures that the patient is fit for surgery. The evaluation may include blood tests, imaging studies, and a review of medical history. Discussing medications and allergies with the surgeon is crucial. This step helps prevent complications during the breast augmentation procedure.
Patients should be honest about their lifestyle choices as well. Smoking or heavy drinking can affect recovery. Surgeons may advise quitting these habits before the surgery. Understanding personal health risks is essential for a successful outcome.
Tissue Expansion
Breast tissue expansion might be necessary prior to surgery. This process prepares the body for fat transfer by stretching the skin and tissue. Surgeons place a tissue expander under the skin. Over time, they gradually fill it with saline solution. This method allows for more natural results after the breast cancer surgery.
The expansion period can take several weeks to months, depending on individual needs. Patients should expect multiple visits to their surgeon during this phase. Each visit involves checking progress and adjusting the expander as needed. Patience is key, as achieving the right size is important for overall satisfaction.
Anesthesia Preparation
Preparing for general anesthesia is another critical step in this process. Anesthesia allows patients to remain comfortable during surgery. Before the procedure, surgeons provide instructions on what to expect. Patients typically receive guidelines about eating and drinking prior to surgery day.
Understanding the surgical plan is vital as well. Surgeons explain how they will perform the fat transfer procedure. This includes discussing where they will harvest fat from the body and how it will be injected into the breast area. Knowing these details helps alleviate anxiety.
Patients should not hesitate to ask questions about any aspect of the procedure. Clear communication with the surgeon fosters trust and understanding. It’s also important to have a support system in place for recovery after surgery.
Recovery Process
Timeline
Recovery from breast reconstruction surgery varies by patient. Most patients spend one night in the hospital after the procedure. During the first week, pain is common but manageable with medication.
By weeks two to three, swelling decreases and daily activities can resume slowly. Patients typically return to work within two to six weeks, depending on their job’s physical demands.
Full recovery may take several months. By this time, patients should see significant improvements in comfort and mobility.
Post-Operative Care
Managing post-operative care is crucial for a successful recovery. Patients should follow their doctor’s specific instructions regarding wound care and activity restrictions.
Keeping the surgical area clean helps prevent infection. Use mild soap and water when cleaning the area. Avoid soaking in baths or swimming pools until cleared by a doctor.
Pain management is vital during recovery. Doctors often prescribe pain medications to help ease discomfort. Over-the-counter options may also be effective once initial pain subsides.
Monitoring for complications is essential. Watch for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge from the incision site. Report any fever or excessive pain to your healthcare provider immediately.
Follow-Up Appointments
Follow-up appointments play an important role in the recovery journey. These visits allow doctors to monitor healing progress and address any concerns.
Patients usually have their first follow-up appointment within one week after surgery. Additional appointments may occur at regular intervals over the next few months.
During these visits, doctors assess the surgical site and check for complications. They can adjust medications or recommend therapies if necessary.
These appointments also provide an opportunity to discuss emotional well-being after surgery. Many patients experience a range of feelings during recovery. Support from healthcare professionals can aid in addressing these emotions effectively.
Final Remarks
Fat transfer for breast reconstruction offers a natural solution to enhance your body confidence. It’s a safe procedure with numerous benefits, from improved aesthetics to a potentially permanent outcome. Understanding the risks and suitability is crucial for making informed decisions.
You deserve to feel empowered in your choices. Consult with a qualified professional to discuss your options and tailor a plan that works for you. Take the next step towards reclaiming your confidence today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is fat transfer for breast reconstruction?
Fat transfer for breast reconstruction involves harvesting fat from another body area and injecting it into the breast to restore volume and shape after surgery or trauma.
How long does the fat transfer procedure take?
The procedure typically takes about 2 to 4 hours, depending on the amount of fat being transferred and the complexity of your case.
Is fat transfer safe for breast reconstruction?
Yes, fat transfer is considered safe when performed by a qualified plastic surgeon. However, like any surgical procedure, it carries some risks that should be discussed with your doctor.
How soon can I return to normal activities after fat transfer?
Most patients can resume light activities within a few days. However, strenuous exercise and heavy lifting should be avoided for at least 2 to 4 weeks.
Will I need multiple sessions for optimal results?
Many patients require multiple sessions to achieve desired results, as not all transferred fat will survive. Your surgeon will provide a personalized plan based on your needs.
Can fat transfer improve breast symmetry?
Yes, fat transfer can enhance breast symmetry by adding volume to one breast or correcting irregularities, providing a more balanced appearance.
How do I choose a qualified surgeon for this procedure?
Look for board-certified plastic surgeons with experience in fat transfer techniques. Check their credentials, reviews, and before-and-after photos to ensure you find a trusted expert.
